Posts
The Unknowns
Thanks to John S for the link. Hooah
Washing the Wall
Wait for the end. A organization on Oct 24, 2015.
Thanks to Charlie, Hooah
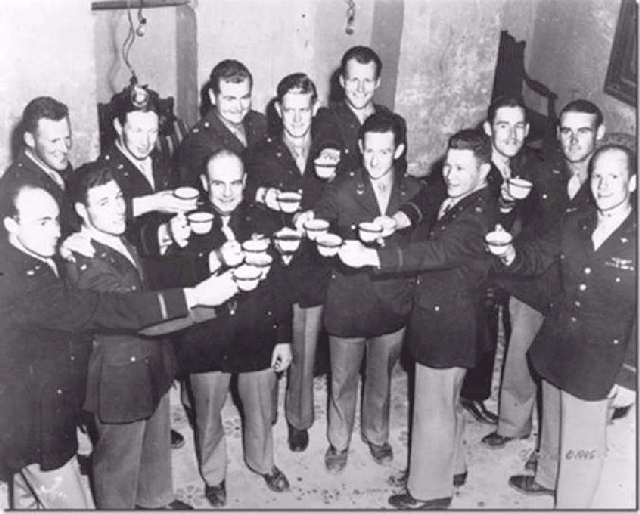
The Final Toast!
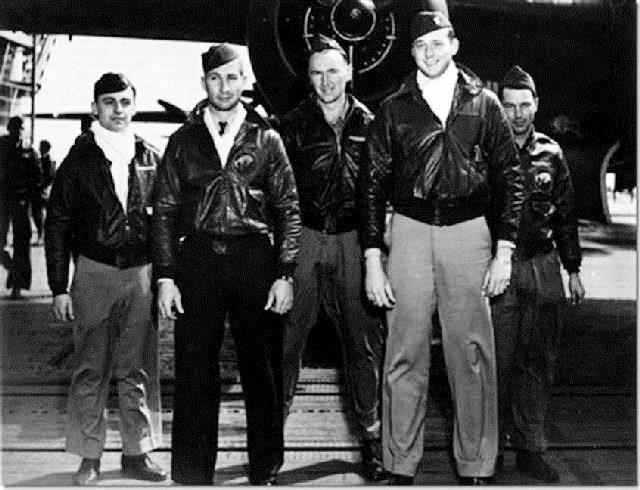
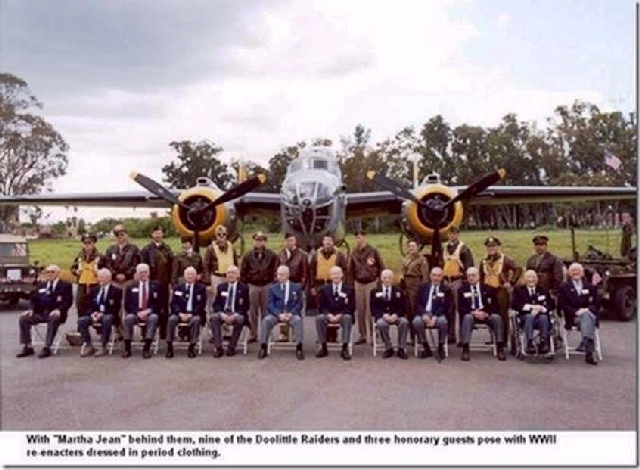
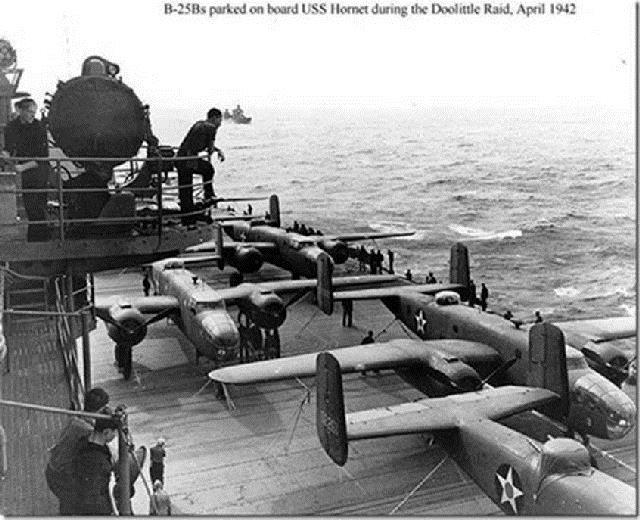
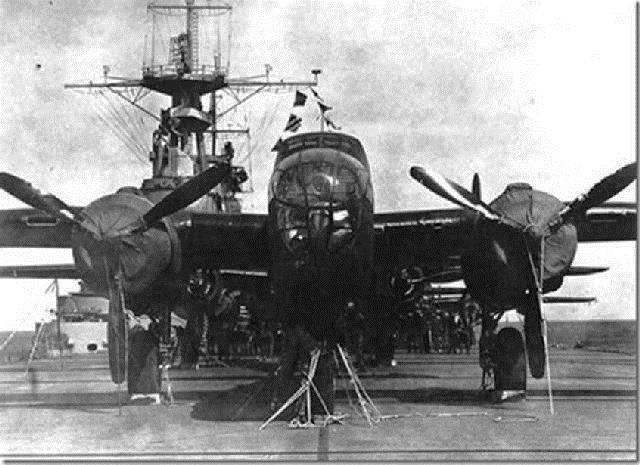
THE FINAL TOAST! They bombed Tokyo 73 years ago.
They once were among the most universally admired and revered men in the United States .. There were 80 of the Raiders in April 1942, when they carried out one of the most courageous and heart-stirring military operations in this nation’s history. The mere mention of their unit’s name, in those years, would bring tears to the eyes of grateful Americans.
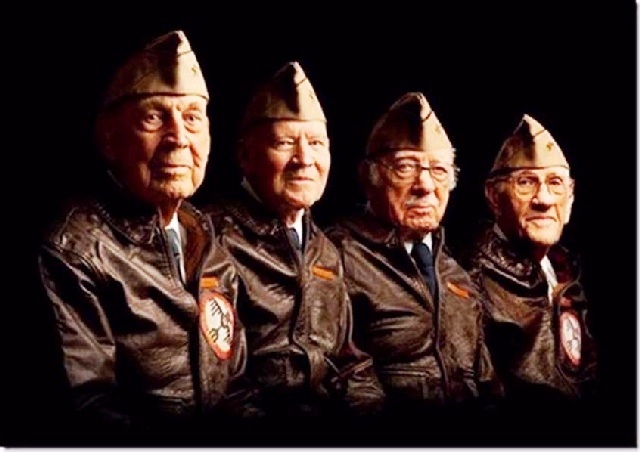
Now only four survive.
After Japan’s sneak attack on Pearl Harbor, with the United States reeling and wounded, something dramatic was needed to turn the war effort around.
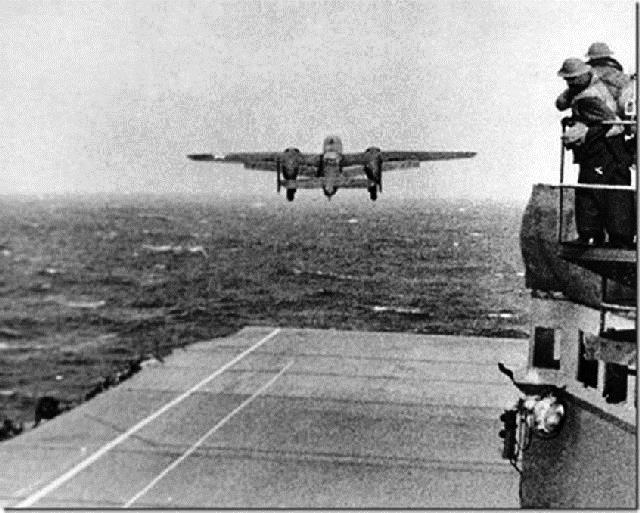
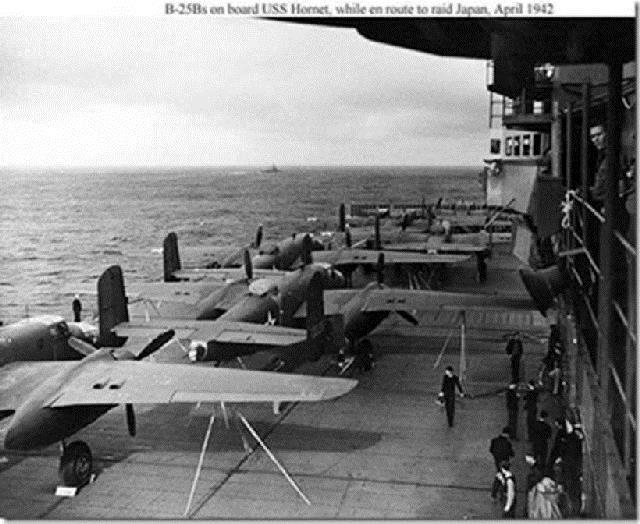
Even though there were no friendly airfields close enough to Japan for the United States to launch a retaliation, a daring plan was devised. Sixteen B-25s were modified so that they could take off from the deck of an aircraft carrier. This had never before been tried — sending such big, heavy bombers from a carrier.
The 16 five-man crews, under the command of Lt. Col. James Doolittle, who himself flew the lead plane off the USS Hornet, knew that they would not be able to return to the carrier. They would have to hit Japan and then hope to make it to China for a safe landing.
But on the day of the raid, the Japanese military caught wind of the plan. The Raiders were told that they would have to take off from much farther out in the Pacific Ocean than they had counted on. They were told that because of this they would not have enough fuel to make it to safety.
And those men went anyway.
They bombed Tokyo and then flew as far as they could. Four planes crash-landed; 11 more crews bailed out, and three of the Raiders died. Eight more were captured; three were executed.
Another died of starvation in a Japanese prison camp. One crew made it to Russia.
The Doolittle Raiders sent a message from the United States to its enemies, and to the rest of the world: We will fight. And, no matter what it takes, we will win.
Of the 80 Raiders, 62 survived the war. They were celebrated as national heroes, models of bravery. Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer produced a motion picture based on the raid; “Thirty Seconds Over Tokyo,” starring Spencer Tracy and Van Johnson, was a patriotic and emotional box-office hit, and the phrase became part of the national lexicon. In the movie-theater previews for the film, MGM proclaimed that it was presenting the story “with supreme pride.”
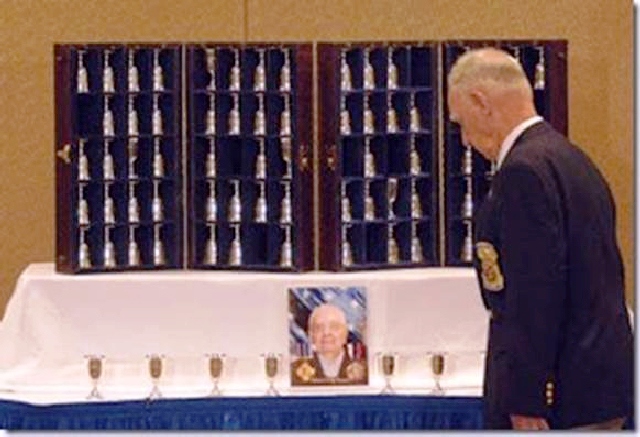
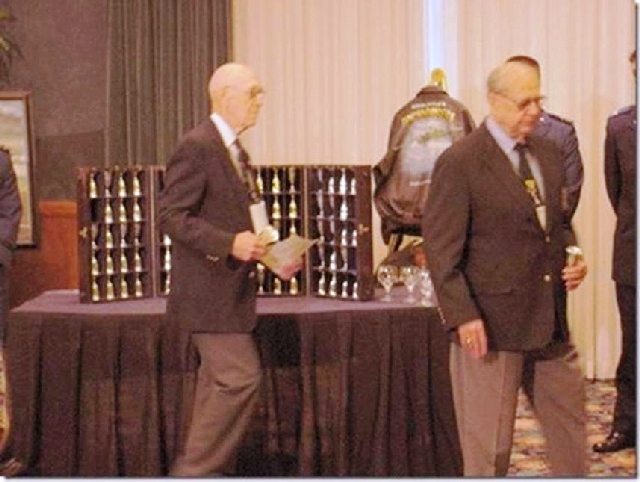
Beginning in 1946, the surviving Raiders have held a reunion each April, to commemorate the mission. The reunion is in a different city each year. In 1959, the city of Tucson, Arizona, as a gesture of respect and gratitude, presented the Doolittle Raiders with a set of 80 silver goblets. Each goblet was engraved with the name of a Raider.
Every year, a wooden display case bearing all 80 goblets is transported to the reunion city. Each time a Raider passes away, his goblet is turned upside down in the case at the next reunion, as his old friends bear solemn witness.
Also in the wooden case is a bottle of 1896 Hennessy Very Special cognac. The year is not happenstance: 1896 was when Jimmy Doolittle was born.
There has always been a plan: When there are only two surviving Raiders, they would open the bottle, at last drink from it, and toast their comrades who preceded them in death.
As 2013 began, there were five living Raiders; then, in February, Tom Griffin passed away at age 96.
What a man he was. After bailing out of his plane over a mountainous Chinese forest after the Tokyo raid, he became ill with malaria, and almost died. When he recovered, he was sent to Europe to fly more combat missions. He was shot down, captured, and spent 22 months in a German prisoner of war camp.
The selflessness of these men, the sheer guts … there was a passage in the Cincinnati Enquirer obituary for Mr. Griffin that, on the surface, had nothing to do with the war, but that was emblematic of the depth of his sense of duty and devotion:
“When his wife became ill and needed to go into a nursing home, he visited her every day. He walked from his house to the nursing home, fed his wife and at the end of the day brought home her clothes. At night, he washed and ironed her clothes. Then he walked them up to her room the next morning. He did that for three years until her death in 2005.”
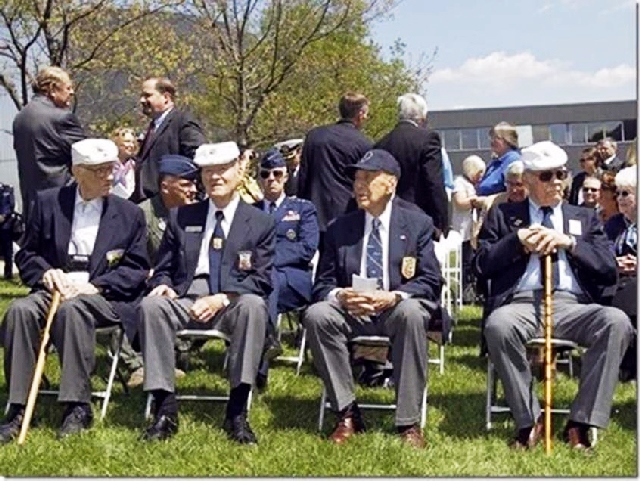
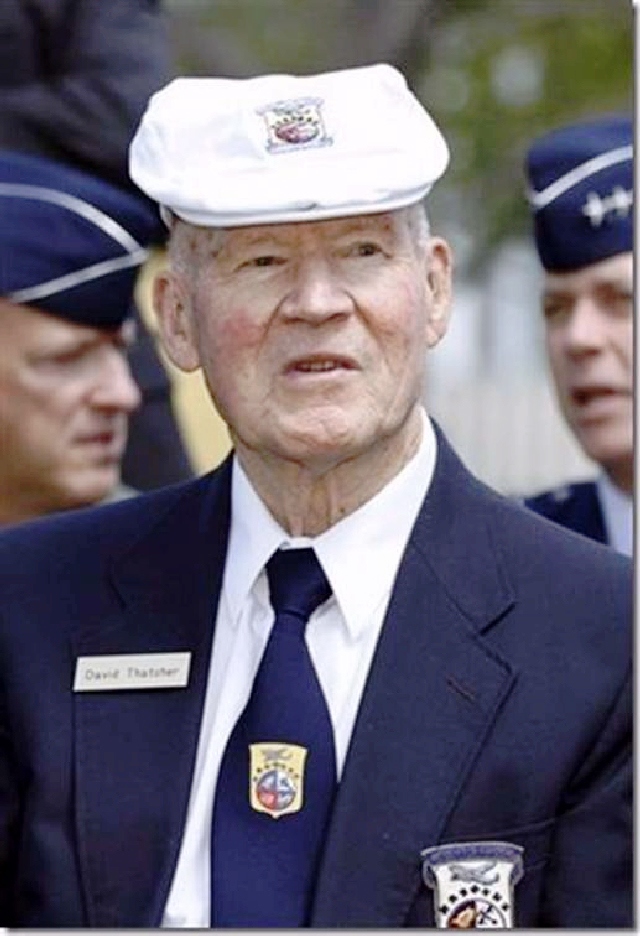
So now, out of the original 80, only four Raiders remain: Dick Cole (Doolittle’s co-pilot on the Tokyo raid), Robert Hite, Edward Saylor and David Thatcher. All are in their 90s. They have decided that there are too few of them for the public reunions to continue.
The events in Fort Walton Beach marked the end. It has come full circle; Florida’s nearby Eglin Field was where the Raiders trained in secrecy for the Tokyo mission. The town planned to do all it can to honor the men: a six-day celebration of their valor, including luncheons, a dinner and a parade.
Do the men ever wonder if those of us for whom they helped save the country have tended to it in a way that is worthy of their sacrifice? They don’t talk about that, at least not around other people. But if you find yourself near Fort Walton Beach this week, and if you should encounter any of the Raiders, you might want to offer them a word of thanks. I can tell you from first hand observation that they appreciate hearing that they are remembered.
The men have decided that after this final public reunion they will wait until a later date — some time this year — to get together once more, informally and in absolute privacy. That is when they will open the bottle of brandy. The years are flowing by too swiftly now; they are not going to wait until there are only two of them.
They will fill the four remaining upturned goblets. And raise them in a toast to those who are gone.
Thanks to Howard S. Hooah
A Tribute to Vietnam Veterans Featuring the Voice of Mr. Sam Elliott
Thanks to Bruce G. Hooah
7 Surprising Facts About the US Army
7 Surprising Facts You Probably Don’t Know About the US Army
The Army is older than the country it serves.
Americans celebrate the birth of their nation as July 4, 1776, but the Army is actually the country’s “big brother.” Which makes sense, considering the Continental Army of 1775 — led by future President George Washington — needed to start beating the British in the colonies so Thomas Jefferson could finally get some time to write.
Before the Army was established, colonists were organized into rag-tag militias with no real structure or unified chain-of-command. But in the spring of 1775, most wanted to attack the British near Boston but knew they needed more structure to confront the professional soldiers on the other side. That’s where the official birth of the Army came in, on June 14, 1775, through a resolution from the Continental Congress.
The next day, George Washington was appointed as commander-in-chief of the new Army, and took command of his troops in Boston on July 3, 1775, according to the Army History Division.
If the U.S. Army were a city, it would be the tenth-largest in the United States.
There are just over one million soldiers currently serving in the Army. Just about half of that number is on active-duty and serving full-time, while the rest make up the reserve components of National Guard and Army Reserve. To put it in perspective, a city filled with soldiers would have more people in it than San Jose, California, Austin, Texas, Jacksonville, Florida, and San Francisco, California. Continue reading
11 Things Trainees Will Complain About
Through the use of insults, strict discipline, sleep deprivation, and controlled explosions, Army drill sergeants turn recent high school grads and civilians looking for a new job into trained soldiers ready to serve in America’s wars. This transition is, of course, painful — by design.
Here are 11 things trainees will complain about before learning to suck it up as an Army soldier:
“I’m tired. I didn’t get enough sleep last night.”
New U.S. Army soldiers are expected to operate on little sleep. While in the barracks, recruits’ sleep is regularly interrupted by drill sergeants conducting inspections, punishing infractions, getting head counts, or waking soldiers for the heck of it. The party continues in the field where soldiers sleep in bags instead of beds.
“This food is terrible.”
Military food is rarely praised, and basic training food is even worse. Eating periods are very short and are supervised by drill sergeants who pounce onto soldiers who reach for fattening or sugary foods. Continue reading